Arthritis Health Effects, its Types, Causes, Symptoms, Effective Remedies, Treatment, Medicine, Possible Complications and FAQ
What is Arthritis?
Arthritis – derived from the Greek word ‘disease of the joints’. It is defined as an acute or chronic joint inflammation that is often associated with pain and structural damage. Arthritis is not synonymous with arthralgia. Arthralgia is a localized pain in the joint regardless of its origin.
The presence of more than 100 different types of arthritis is described; the most common one is Osteoarthritis or Degenerative Arthritis which is non-inflammatory arthritis.
Arthritis Health Effects and Treatment
Inflammatory arthritis can occur in several settings and inflammation can cause by –
- Autoimmune process (Rheumatoid arthritis, Psoriatic arthritis, Ankylosing spondylitis, etc.),
- By crystal deposition (Gout, Pseudogout, Basic calcium phosphate disease)
- Infection (Septic arthritis, Lyme’s arthritis).
Inflammatory arthritis can also be accompanied by other autoimmune connective tissues such as Systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren Syndrome, Scleroderma, Myositis, Inflammatory bowel disease, Celiac disease.
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. Between 19% and 30% of adults over the age of 45 have knee osteoarthritis, 27% have osteoarthritis of the hand and 27% have hip osteoarthritis. It is estimated that 40% of men and 47% of women develop osteoarthritis in their lifetime, with the incidence increasing to 60% if they have a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 30.
The following article discusses the health effects of Arthritis and its complications along with other related and important things.
Also Read: 15+ Amazing Health Benefits of Chirata, Uses, and Side Effects
Health Affecting Types of Arthritis
Arthritis has 6 common types, they are as follows-
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Childhood arthritis
- Fibromyalgia
- Gout
- Lupus
Causes & Symptoms of Arthritis
The causes and health affecting symptoms of arthritis are varied depending on its type.
- Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. Symptoms frequently occur in hands, hips and knees. In osteoarthritis, the cartilage inside the joint begins to break and the underlying bone begins to change. These changes usually develop slowly and the situation worsens over time.
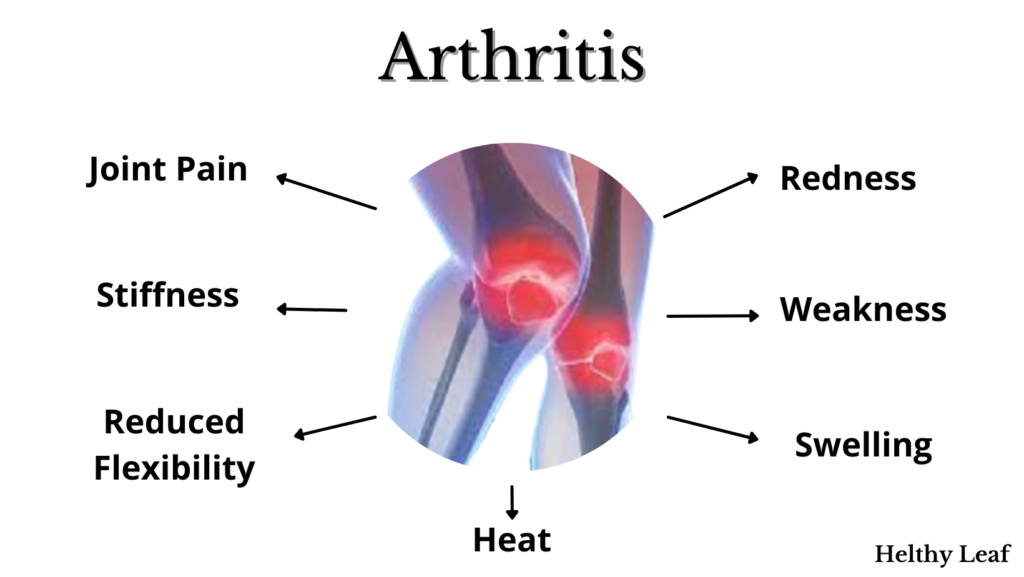
Causes- Joint cartilage between bones is damaged or broken.
Symptoms-
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Decrease range of motion or flexibility
- Swelling
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune and inflammatory disease, which means your immune system accidentally attacks healthy cells in your body causing inflammation (painful swelling) in the affected parts of the body.
It mainly attacks joints, usually many joints at the same time. It usually affects the hands, wrists and knee joints. With this, the lining of the joints becomes inflamed, causing damage to joint tissue. It results in chronic pain, unsteadiness (lack of balance), and deformity. It can also affect other tissues throughout the body and cause problems in organs such as lungs, heart and eyes.
Cause- Rheumatoid arthritis is the result of an immune response in which the body’s immune system attacks its own healthy cells. The specific causes are unknown, but some factors may increase the risk of developing the disease.
Symptoms-
- Pain in multiple joints
- Stiffness in multiple joints
- Tenderness and swelling in multiple joints
- Similar symptoms on both sides of the body (e.g. both hands or both knees)
- Weight loss
- fever
- fatigue
- weakness
- Childhood Arthritis
Arthritis in children is called childhood arthritis or adolescent arthritis. The most common form of childhood arthritis is adolescent idiopathic arthritis (JIA-Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis), also known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Childhood arthritis can cause permanent physical damage to the joint. This damage can make it difficult for the child to do everyday tasks like walking or dressing-up and can lead to disability.
Causes- The exact cause of childhood arthritis is unknown. The immune system may not function properly in childhood arthritis leading to inflammation in the joints and other systems of the body.
Symptoms-
- Joint pain
- Swelling
- Fever
- Stiffness
- Rash
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Inflammation of the eyes
- Activities of daily living such as walking, dressing, and difficulty in playing.
- Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a condition that causes pain throughout the body. People with fibromyalgia may be more sensitive to pain than people without fibromyalgia. This is called abnormal pain perception processing.
Causes- The cause of fibromyalgia is not known, but it can be treated and managed effectively.
Symptoms-
- Pain and stiffness all over the body
- Fatigue
- Depression and Anxiety
- Sleep problems
- Problems with thinking, memory and concentration
- Headache including migraine
- Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
- Mouth or jaw pain, including a jaw disorder known as symptoms of temporomandibular joint syndrome (TJM)
- Digestive problems, such as abdominal pain, swelling, constipation, and even irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Gout
Gout is a common form of inflammatory arthritis that is very painful. It usually affects one joint at a time. Sometimes the symptoms are worse, called flare, and sometimes show no symptoms. Repeated gout can lead to gout arthritis, a worsening form of arthritis.
Causes- Gout is caused by a condition called hyperuricemia, which causes excessive uric acid in the body. Uric acid is produced when the body breaks down purines, which are found in your body and in the food you eat. When the body has too much uric acid, uric acid crystals (monosodium urate) can accumulate in the joints, fluids and tissues inside the body.
Hyperuricemia does not always cause gout, and it does not need to be treated without symptoms of gout.
Symptoms-
- Usually severe pain
- Swelling
- Redness
- Heat
- Lupus
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) arthritis is the most commonly seen type of lupus. Its an autoimmune disease in which the immune system attacks its own tissues causing widespread inflammation and tissue damage in the affected organs. Almost all joints may be affected by SLE, but hand and knee involvement is most common.
Causes- The causes of SLE are unknown, but are believed to be related to environmental, genetic and hormonal factors.
Symptoms- People with SLE may experience various symptoms including fatigue, skin rashes, fever, and joint pain or swelling. In some adults, having a period of SLE symptoms – called flare – can occur every time, sometimes at intervals of another year, and may move away at other times – called remission. However, other adults may experience SLE flare more often throughout their lives.
In addition, sensitivity to the sun, mouth ulcers, arthritis, lung problems, heart problems, kidney problems, seizures, psychosis, and blood cells and immunological abnormalities can also appear.
Also Read: Immune System of Human Body
Remedies for Arthritis
- Aquatic exercise: Can be beneficial for people with arthritis problems. Water creates resistance, which helps in increasing the intensity of exercise. Doing so reduces arthritis pain.
- Weight loss: Increased pressure causes the cartilage between the joints to break down more quickly, leading to a deterioration of osteoarthritis. Weight loss reduces stress on the joints, as well as pain and stiffness.
- Yoga: Iyengar yoga is a type of yoga that focuses on the right physical alignment and relieves tension and inflammation from the body.
- Hot/cold compress: Both taking hot and cold compress are different but effective methods to reduce arthritis pain. Heat therapy increases blood circulation and can soothe stiff joints and aching muscles; Cold treatment, on the other hand, limits blood vessels, which reduce circulation, reduce swelling, and numb pain. You may apply heat and cold compress alternatively, but the damage caused by these treatments is essential to carefully monitor the skin and stop using them if it hurts.
- Try Meditation: Meditation can control pain and stress, which can both compromise the immune system.
- Massage: Regular massage on muscles and joints can help relieve pain and other problems caused by arthritis. Experts believe massage reduces the production of body pressure hormone cortisol and neurotransmitter substance P, which is associated with pain. Massage helps in improving mood by increasing serotonin levels.
- Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS) is a method of pain relief that uses electrodes in the form of stickpads attached to the skin surface to provide small electrical current to the body.
- Take enough vitamin D. Vitamin D forms strong bones and helps in maintaining the functioning of the immune system.
- Eat omega-3 fatty acids. Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids help reduce inflammation in the body and play a role in controlling the immune system.
- Some people take chondroitin sulfate or glucosamine hydrochloride for osteoarthritis.
Also Read: 12+ Effective Ways to Fight Obesity and Related Problem
Complications of Arthritis
Severe arthritis, especially if it affects your hands or arms, can make it difficult for you to do everyday tasks. Arthritis in weight bearing joints can prevent you from walking easily or sitting straight. In some cases, joints can gradually distort their alignment and shape.
Conclusion
The information carried by the above article about the health effect of arthritis and related things to it, is based on trusted sources and provided only for knowledge purposes and not meant for replacing professional health care treatment. In case of severe situations it is recommended to consult professionals and seek medical treatment for appropriate results.
Also Read: Arthritis & Treatment (Assamese)
FAQ
1) Does SLE run in the family?
A- Most people with SLE do not have it in the family; however, some people with SLE do have a family history of the disease. Men and women with close family members with SLE are at a slightly higher risk of getting the disease.
2) What is the most common type of arthritis?
A- Common types of arthritis include rheumatoid arthritis, gout, fibromyalgia and osteoarthritis.
3) Can I get arthritis?
A- Some factors make you more likely to have arthritis. You can control some risk factors, and others you cannot control. By avoiding or controlling the risk factors, you can reduce your risk of developing arthritis or worsening arthritis.
4) Can arthritis be prevented?
A- Arthritis cannot be prevented but you can reduce the risk of developing certain types of arthritis and its health damaging symptoms by avoiding or controlling the risk factors. Risk factors include-
- Being overweight or obese
- Joint injuries
- Smoking.
5) Can I exercise with arthritis?
A- Yes, you can. Arthritis-friendly physical activity is good for people with arthritis.
